
Chih-Yao Ma*, Min-Hung Chen*, Zsolt Kira, and Ghassan AlRegib
Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2018
[arXiv] [GitHub]
(* equal contribution)
In this work, we demonstrate a strong baseline two-stream ConvNet using ResNet-101. We use this baseline to thoroughly examine the use of both RNNs and Temporal-ConvNets for extracting spatiotemporal information. Building upon our experimental results, we then propose and investigate two different networks to further integrate spatiotemporal information: 1) temporal segment RNN and 2) Inception-style Temporal-ConvNet.
Our analysis identifies specific limitations for each method that could form the basis of future work. Our experimental results on UCF101 and HMDB51 datasets achieve state-of-the-art performances, 94.1% and 69.0%, respectively, without requiring extensive temporal augmentation.

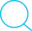
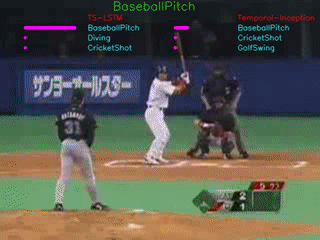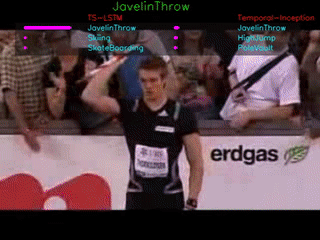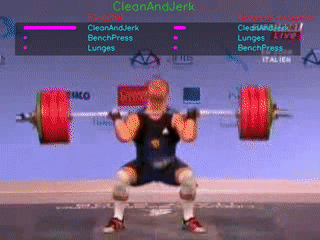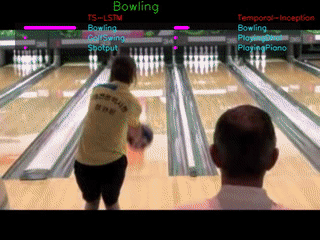
The GIFs demonstrate the top-3 predictions results of our TS-LSTM and Temporal-Inception methods. The text on the top is the ground truth, three texts are the predictions for each of the method, and the bar right next to the predictions are how confident the model makes predictions.





If you find this work useful, please cite our paper:
@article{ma2018ts,
title={TS-LSTM and temporal-inception: Exploiting spatiotemporal dynamics for activity recognition},
author={Ma, Chih-Yao and Chen, Min-Hung and Kira, Zsolt and AlRegib, Ghassan},
journal={Signal Processing: Image Communication},
year={2018},
publisher={Elsevier}
}